Gingivitis is a common condition that affects the gums. Caused by plaque buildup along the gum line, gingivitis can lead to inflammation and redness. If left untreated, it can lead to periodontal disease, which can seriously affect your oral health. There are specific steps you can take to prevent and treat gingivitis. This blog post will discuss gingivitis, its symptoms and causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention tips.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease that affects the gums around your teeth. It’s caused by a buildup of plaque along the gum line, leading to inflammation and redness in the gum tissue. If left untreated, it can progress into periodontal (gum) disease, which can cause tooth loss and other serious health problems if not treated promptly.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
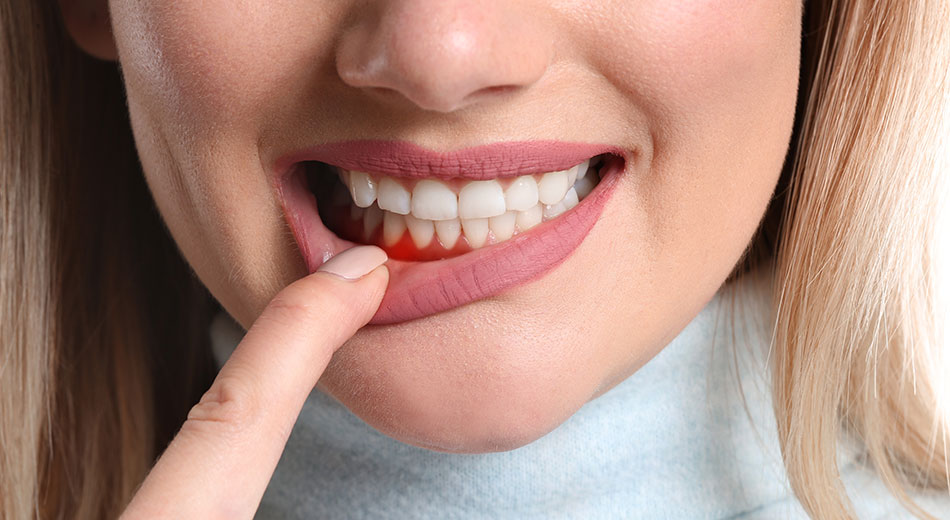
The most common symptom of gingivitis is bleeding when brushing or flossing your teeth. Other symptoms may include redness or swelling in the gums, bad breath that won’t go away even after brushing and flossing regularly, receding gums (where they appear to be pulling away from your teeth), and tenderness or pain in your gums when eating or drinking cold items such as ice cream or soda.
Causes & Risk Factors for Developing Gingivitis
The leading cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene caused by inadequate brushing and flossing habits combined with a buildup of bacteria on the teeth and gums due to foods containing sugars or starches like bread, pasta, chips, etc. Certain medical conditions may also increase your risk for developing gingivitis, such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS, as well as certain medications, such as birth control pills. Smoking also increases your risk of developing this condition due to decreased blood flow in the mouth area which makes it harder for your body to fight off infection-causing bacteria.
Diagnosis of Gingivitis
A dentist will diagnose you with gingivitis based on an examination of your mouth, including any signs of inflammation or redness in the gum tissue and any bleeding when brushing or flossing. They may also order specific tests such as x-rays to get a better look at any possible bone damage caused by periodontal disease if present.
Treatment Options for Gingivitis
The treatment options for gingivitis depend on how severe it is. Generally, they involve improved oral hygiene habits such as daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste twice daily as well as flossing once daily combined with professional cleanings from a dentist every six months where they will remove any built-up plaque from between your teeth that you cannot reach with regular brushing/flossing alone.
Antibiotics may also be prescribed if needed, along with prescription mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine gluconate (CHX), which helps kill bacteria in hard-to-reach areas that regular cleaning cannot reach. Laser therapy has also been used successfully to kill bacteria in some cases. However, this is not always recommended due to potential side effects associated with laser treatments, so talk with your dentist about whether this option would suit you before proceeding.
How to Prevent Gingivitis
When it comes to preventing and treating gingivitis, there are several steps one can take toward maintaining good oral health. By practicing good oral hygiene at home combined with professional cleanings from a dentist every six months, taking antibiotics if needed, using prescription mouthwashes containing CHX, considering laser therapy depending on severity, quitting smoking if applicable, changing out toothbrushes more frequently (every 3- 4 months) & eating healthy foods high in vitamins B12&C one can do their part towards guarding against this condition. With awareness & actionable preventive measures, anyone can take charge of their dental health!